Meta TechX Engineers: Learn how to design gears for hot rolling mills using the required parameters, formulas, and essential insights from industry professionals. Discover the key factors that contribute to successful gear design in this in-depth article.
Introduction:
Designing gears for hot rolling mills requires meticulous attention to detail, expertise, and an understanding of the parameters and formulas involved. The perfect gear design ensures smooth and efficient operation, minimizing wear and tear while maximizing productivity. In this article, we will explore the essential aspects of gear design for hot rolling mills, providing you with valuable insights and expert tips to achieve optimal results.
Design Gears for Hot Rolling Mills: Key Parameters
Gears play a pivotal role in the operation of hot rolling mills, transmitting power and torque smoothly between the driving and driven components. To design gears effectively, it is crucial to consider the following parameters:
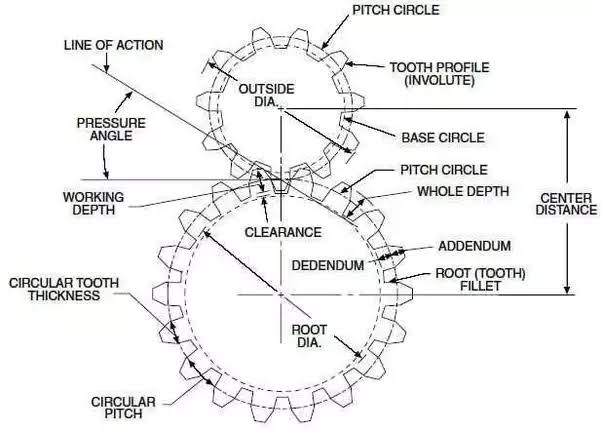
- Module:
The module represents the size of the gear teeth and is an essential parameter in gear design. It determines the pitch diameter, contact ratio, and tooth strength. Selecting an appropriate module is vital for achieving the desired gear performance. - Pressure Angle:
The pressure angle determines the angle of the tooth profile, affecting the load-carrying capacity and efficiency of the gears. Common pressure angles include 20° and 14.5°, with the former being widely used in hot rolling mill gear design. - Face Width:
The face width defines the width of the gear tooth, influencing its load-carrying capacity and surface contact area. Adequate face width ensures efficient power transmission and minimizes the risk of failure or premature wear. - Gear Ratio:
The gear ratio determines the speed and torque relationship between the driving and driven components. Analyzing the desired output and selecting the appropriate gear ratio is critical for achieving the desired rolling mill performance.
Design Gears for Hot Rolling Mills: Essential Formulas
To design gears for hot rolling mills accurately, it is essential to utilize the following formulas: - Pitch Diameter (D):
The pitch diameter represents the effective diameter of a gear. It can be calculated using the formula:
D = M * Z,
where M is the module and Z is the number of teeth on the gear. - Gear Ratio (GR):
The gear ratio defines the proportion between the driving and driven components in terms of speed and torque. It can be calculated as:
GR = N1 / N2,
where N1 is the number of teeth on the driving gear and N2 is the number of teeth on the driven gear. - Tooth Thickness (T):
The tooth thickness refers to the radial dimension of a gear tooth. It can be calculated using the formula:
T = (π * D) / Z,
where D is the pitch diameter and Z is the number of teeth.
H2: Expert Tips for Gear Design in Hot Rolling Mills
Achieving an impeccable gear design for hot rolling mills requires expertise and industry experience. Here are some expert tips to ensure success: - Optimize Gear Material:
Choose the appropriate gear material based on factors like load capacity, operating temperature, and wear resistance. Popular materials for hot rolling mill gears include alloy steels, case-hardened steels, and cast iron. - Consider Lubrication and Cooling:
Effective lubrication and cooling systems are vital for minimizing friction and heat generation, ensuring smooth gear operation. Incorporate features like oil channels, spray nozzles, and cooling fins into the gear design to enhance performance and prolong gear life. - Conduct Finite Element Analysis (FEA):
Utilize FEA techniques to simulate gear performance under different load conditions. This enables you to identify potential stress concentrations, optimize gear geometry, and enhance gear design before its actual implementation. - Perform Rigorous Testing:
After finalizing the gear design, conduct rigorous testing under load conditions similar to real-world scenarios. This helps ensure the gear’s performance, durability, and reliability, reducing the risk of unexpected failures.
Conclusion:
Designing gears for hot rolling mills demands a deep understanding of the parameters, formulas, and expert tips discussed in this article. By considering the key parameters, utilizing the appropriate formulas, and implementing expert insights, you can create gears that deliver efficient power transmission, prolong the life of the mill, and optimize productivity. Keep refining your gear design approach based on industry advancements, and your rolling mill will continue to operate smoothly and reliably.