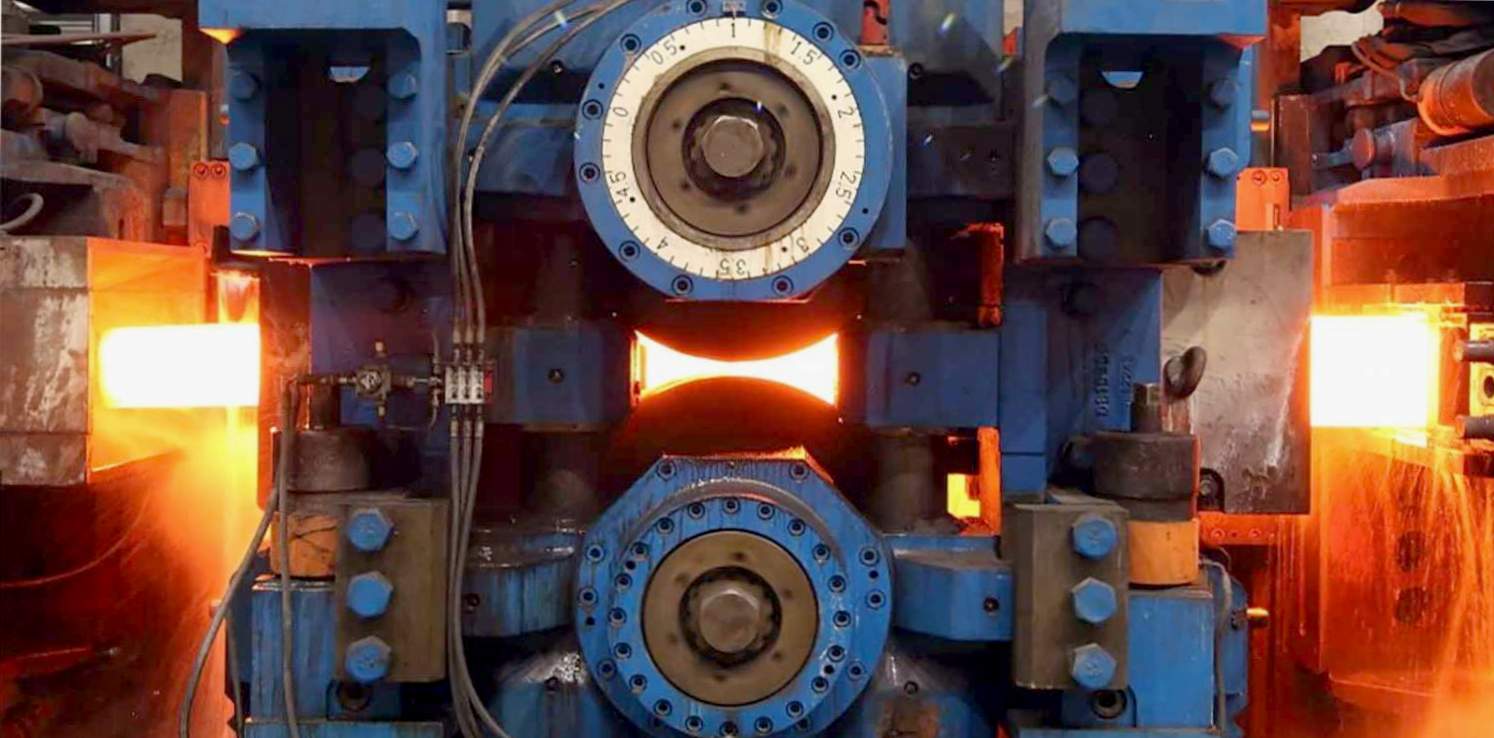
Hot Rolling Mill
Hot rolling is a fundamental process in the steel industry. It involves the heating and shaping of metal ingots or billets to produce various forms of steel products. The process begins with the heating of the metal to a high temperature, which makes it easier to shape and mold. Once heated, the metal is passed through a series of rollers that apply pressure and force to shape it into the desired form, such as Sheets, Bars or Rods Etc.. This process helps improve the mechanical properties of the metal, making it stronger and more durable. Hot rolling mills play a crucial role in the production of steel, providing the necessary means to transform raw materials into useful and versatile products for various industries.
Types of Hot Rolling Mill…
Hot rolling mills are used in the manufacturing industry to shape and form metal at high temperatures. There are different types of hot rolling mills, each designed for specific purposes and with unique specifications. One common type is the two-high rolling mill, which consists of two rolls that rotate in opposite directions, applying pressure to the metal to reduce its thickness and increase its length. Another type is the three-high rolling mill, which has three rolls and is commonly used for making structural shapes like beams and channels. The four-high rolling mill has four rolls and provides greater flexibility in terms of thickness and shape control. Finally, the cluster rolling mill consists of multiple rolls arranged in a cluster, allowing for increased production and efficiency. These different types of hot rolling mills cater to the diverse needs of the manufacturing industry, ensuring precise and efficient metal forming processes.
Hot Rolling Process…
Hot rolling is a method used in the manufacturing industry to shape metals. It involves Re-heating the metal to a high temperature (1080°C to 1150°C) and then passing it through a series of rollers to achieve the desired shape and thickness. This process is commonly used for the production of steel, aluminum, and other metals. The heated metal is fed into the rollers, which apply Pressure and Force, causing the metal to Deform and take on the shape of the rollers. As the metal passes through each set of rollers, it becomes thinner and longer, ultimately reaching the desired thickness and shape. Hot rolling is an efficient and cost-effective method for producing high-quality metal products with excellent mechanical properties.
Major Machineries used in Hot Rolling Mill…
Hot rolling mills are equipped with various machineries that play a crucial role in the production process. These machineries are designed to handle the high temperatures and heavy loads involved in hot rolling. One of the key machines is the Re-Heating furnace, which heats the raw materials to the required temperature for rolling. The Roughing mill then reduces the thickness of the heated material through a series of Rollers, while the Finishing mill further refines the thickness and shape. Other important machines include the Shearing machine, which cuts the rolled material into desired lengths, and the Cooling bed, which cools and stabilizes the finished product. Additionally, there are machines for Straightening, Inspection, and Bundling. All of these machineries work together seamlessly to ensure efficient and precise hot rolling processes.
Basic Terms of Rolling Practice…
- 1-Rolling Temperature
- 2-Rolling Pass
- 3-Angle of Bite
- 4-Stress and Strain
- 5-Rolling Draft
- 6-Rolling Load (Actual)
- 7-Rolling Force (Required)
- 8-Torque (Required)
1-Rolling Temperature…
The ideal hot rolling temperature refers to the optimal temperature at which a metal is rolled into its desired shape. This temperature plays a crucial role in determining the success of the rolling process. When the metal is heated to the ideal temperature, it becomes more malleable and easier to shape without cracking or breaking. Additionally, the hot rolling temperature affects the overall efficiency of the process. If the temperature is too low, the metal may not achieve the desired shape, leading to product defects. On the other hand, if the temperature is too high, it can result in excessive energy consumption and decreased material strength. Therefore, finding the ideal hot rolling temperature is vital for achieving high-quality, defect-free metal products.
2-Roll Pass and Design…
Roll pass design is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process in certain industries, such as metalworking. It refers to the planning and arrangement of the passes that a material undergoes during the rolling process. Each pass gradually reduces the thickness and shapes the material into the desired form. The design of the roll pass has a significant impact on the final product’s quality, as it determines the distribution of strain and stress on the material. A well-designed roll pass ensures uniform deformation and minimizes defects, such as cracks or surface imperfections. It also affects the production efficiency by optimizing the use of energy and reducing the number of passes needed. Therefore, a thorough understanding of roll pass design is crucial for achieving desired outcomes in rolling operations.
3-Angle of Bite…
The angle of bite in the hot rolling process refers to the angle at which the incoming material is fed into the rolling mill. It plays a crucial role in determining the quality and efficiency of the rolling process. A proper angle of bite ensures that the material is securely held between the rolls, preventing slipping or skidding. This allows for a more uniform and controlled deformation of the material, resulting in improved product quality. Additionally, the angle of bite affects the amount of force needed for the rolling process. A larger angle of bite requires a lower force, reducing the power consumption and wear and tear on the rolling mill. On the other hand, a smaller angle of bite increases the force required, which can lead to increased energy consumption and decreased productivity. Therefore, selecting an optimal angle of bite is essential for achieving desired rolling outcomes.
4-Stress and Strain…
Stress and strain in hot rolling refer to the forces and deformations experienced by a material during the process of hot rolling, which is a metal working technique used to shape and form metal at high temperatures. Stress is the internal resistance or force per unit area within a material, while Strain is the measure of deformation or change in shape of the material. To calculate Stress in hot rolling, one needs to consider the applied force, the cross-sectional area of the material, and the temperature. Strain, on the other hand, can be calculated by measuring the change in length of the material divided by its original length. Both stress and strain are important parameters in hot rolling as they determine the material’s behavior and performance during the process.
5-Rolling Draft…
Hot rolling draft refers to the reduction in thickness or size of a metal or alloy during the hot rolling process. It is the amount by which the initial thickness is decreased as the material passes through the rolling mill. The hot rolling draft plays a crucial role in shaping the final product’s dimensions and properties. By applying pressure and heat, the metal undergoes plastic deformation, resulting in a thinner and longer product. The hot rolling draft also helps improve the material’s homogeneity and eliminate any surface defects, enhancing its overall quality. Hot rolling draft is carefully calculated and controlled to achieve the desired product specifications.
To calculate the hot rolling draft, you need to measure several factors. First, determine the initial thickness of the metal sheet or strip. Then, measure the final desired thickness. Next, calculate the difference between these two values. This difference represents the draft amount. Additionally, consider the reduction in thickness that occurs during the rolling process. This reduction is typically expressed as a percentage. Multiply the draft amount by this reduction percentage to determine the final hot rolling draft. It is important to note that the hot rolling draft can vary based on various factors such as the type of material, the rolling temperature, and the required properties of the final product. Therefore, it is crucial to consider these factors and make adjustments accordingly.
6-Rolling Load…
Rolling load in hot rolling refers to the force exerted on the workpiece as it passes through the rolling mill. This load is crucial in determining the effectiveness and efficiency of the operation. To calculate the rolling load, several factors need to be considered. First, the material properties of the workpiece, such as its width, thickness, and yield strength, Additionally, the speed and reduction ratio of the rolling mill play a significant role in determining the rolling load. The rolling load can be calculated using mathematical formulas that incorporate these variables. By accurately calculating the rolling load, engineers can optimize the rolling process, ensuring the desired quality and productivity.
7-Rolling Force…
Rolling force in hot rolling refers to the amount of force required to deform the metal in the rolling process. It is a crucial parameter that determines the success and efficiency of the operation. The rolling force depends on various factors such as the material properties, initial thickness, final thickness, and the type of mill being used. The formula to calculate the rolling force involves considering the frictional force, the reduction in thickness, and the width of the material being rolled. This formula helps in predicting the force required, enabling the mill operators to optimize the process parameters and ensure the desired quality of the rolled product. Accurate calculation of rolling force is essential to prevent equipment damage, control energy consumption, and achieve desired output.
Rolling Load and Force…
Rolling load refers to the amount of force exerted on the workpiece during the hot rolling process. It is essential to understand and calculate this load accurately to ensure the efficiency and quality of the rolling operation. The rolling force, on the other hand, pertains to the force required to deform the metal as it passes through the rolling mill. It depends on various factors such as the material properties, temperature, and the reduction in thickness desired. To calculate the rolling load and rolling force, one must consider parameters such as the width of the workpiece, the rolling speed, the coefficient of friction, and the diameter of the rolls. By utilizing these inputs and employing established formulas, engineers can determine the required load and force, enabling them to optimize the hot rolling process for optimal results.
8-Torque…
Torque in hot rolling refers to the force required to rotate the rolls in a mill during the hot rolling process. It is a crucial parameter that determines the efficiency and effectiveness of the rolling operation. The torque can be calculated by considering various parameters such as the diameter of the rolls, the friction between the rolls and the material being rolled, the speed of the rolls, and the temperature of the material. These factors directly influence the amount of force needed to deform and shape the material. By accurately calculating the torque, engineers can optimize the rolling process and ensure consistent quality and productivity. Therefore, understanding the concept of torque in hot rolling and the parameters involved is essential for achieving desired results in the manufacturing industry.

Prashant Goswami