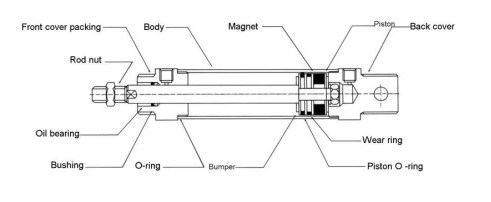
A pneumatic cylinder is a mechanical device that converts the energy from compressed air into linear or rotary motion. It typically consists of a piston, rod, and cylinder, with compressed air acting as the driving force. Pneumatic cylinders are commonly used in a wide range of industrial applications, including automation, packaging, and material handling. One of the primary advantages of using a pneumatic cylinder is its simplicity and reliability. It is easy to install and operate, with minimal maintenance requirements compared to other types of actuators. Additionally, pneumatic systems are well suited for applications where high force and speed are required, such as in manufacturing operations. There are several types of pneumatic cylinders, including single-acting cylinders, double-acting cylinders. The choice of cylinder type depends on the specific application requirements, such as speed, force, and stroke. When using a pneumatic cylinder, it is important to ensure proper installation, maintenance, and safety procedures are followed. The compressed air source must be clean, dry, and at the correct pressure for the cylinder’s operating specifications. Additionally, proper mounting and alignment, actuation, speed and force regulation, lubrication, and temperature control are essential for efficient and safe operation.
Overall, pneumatic cylinders are a versatile and reliable choice for industrial motion control applications, offering fast and efficient performance, simplicity, and low maintenance requirements.
A pneumatic cylinder is a device that converts compressed air into linear motion. Here are some operating guidelines for pneumatic cylinders:
- Safety: Prioritize safety when operating pneumatic cylinders. Make sure to follow all safety guidelines and regulations provided by the manufacturer. This may include wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and ensuring proper installation and maintenance procedures.
- Compressed air source: Ensure that the compressed air source is clean, dry, and at the correct pressure for the pneumatic cylinder’s operating specifications. Use a filter, regulator, and lubricator (FRL) unit as needed to remove contaminants and regulate air pressure.
- Mounting and alignment: Properly mount and align the pneumatic cylinder to ensure efficient and smooth operation. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for mounting and securing the cylinder.
- Actuation: Activate the pneumatic cylinder using a control device such as a valve or solenoid. Ensure that the actuation method is properly set up and functioning correctly.
- Speed and force: Adjust the speed and force of the pneumatic cylinder as required for the application. This is typically done by regulating the air pressure and flow rate. Avoid exceeding the recommended operating limits to prevent damage to the cylinder.
- Lubrication: Some pneumatic cylinders may require lubrication to reduce friction and maintain smooth operation. Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for the appropriate type and frequency of lubrication.
- Temperature: Consider the operating temperature range of the pneumatic cylinder and make sure it is within the specified limits. Extreme temperatures can affect the performance and lifespan of the cylinder.
- Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain the pneumatic cylinder to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Check for leaks, wear and tear, and replace any damaged or worn-out components as necessary. Clean the cylinder and other associated parts to remove dirt, dust, and debris.
It is crucial to refer to the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines specific to the pneumatic cylinder model you are using. These guidelines are general recommendations and may vary depending on the cylinder’s design and application.