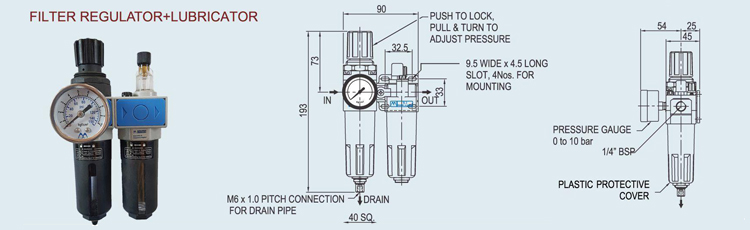
An FRL unit is a combination device consisting of a Filter (F), Regulator (R), and Lubricator (L) that is used to ensure clean air and protection of downstream equipment, regulation of air pressure, and lubrication of moving parts in a compressed air system. The filter removes contaminants and moisture from the compressed air, the regulator adjusts the air pressure to the desired level, and the lubricator adds a controlled amount of oil to the air for lubrication of downstream components. FRL units can be purchased as individual components or combined into a single unit.
Operating and maintaining a pneumatic cylinder is crucial to ensure its longevity and optimal performance. Here are some guidelines to follow:
- Installation: Start by properly installing the pneumatic cylinder to guarantee smooth operation. Ensure it is securely mounted and aligned with the other components of the pneumatic system.
- Lubrication: Regularly lubricate the pneumatic cylinder according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Use the appropriate type and amount of lubricant to minimize friction and wear on the cylinder’s moving parts.
- Air Quality: Ensure that the compressed air supplied to the pneumatic cylinder is clean and dry. Installing filters and dryers in the air system helps prevent the cylinder from exposure to contaminants and moisture.
- Pressure Regulation: Adjust the pressure supplied to the pneumatic cylinder to the recommended range specified by the manufacturer. Avoid exceeding the maximum operating pressure, as it may result in damage or a safety hazard.
- Stroke Adjustment: Depending on the application, it may be necessary to adjust the stroke length of the pneumatic cylinder. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to set the desired stroke accurately.
- Safety Measures: Implement proper safety measures, such as installing appropriate guards and safety valves. Ensure that the cylinder is not subjected to excessive loads or side forces that could lead to damage or malfunction.
- Regular Inspection: Periodically inspect the pneumatic cylinder for signs of wear, leakage, or damage. Pay attention to the seals, rod, mounting brackets, and other critical components. Promptly address any issues that arise.
- Cleanliness: Keep the exterior of the pneumatic cylinder clean and free from debris. This prevents unwanted particles from entering the cylinder and causing damage.
Remember, if you encounter any specific operational or maintenance concerns with your pneumatic cylinder, refer to the manufacturer’s documentation or consult with a qualified technician for assistance.