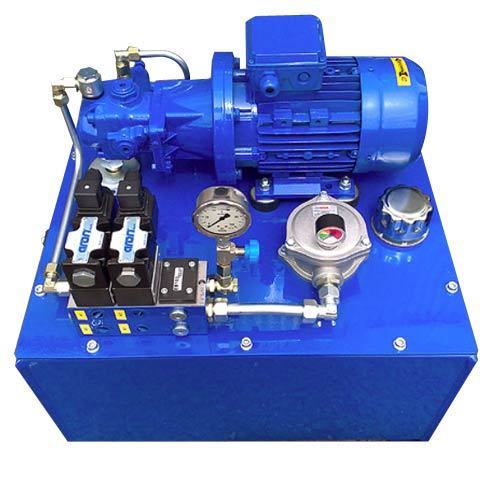

Hydraulic Power Unit (HPU) is a piece of equipment that generates and transfers hydraulic energy to other hydraulic components within a system. It is commonly used to power hydraulic machinery and equipment. The main components of a hydraulic power unit include:
- Hydraulic Pump: It creates flow by converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy. There are different types of pumps, such as gear pumps, vane pumps, and piston pumps.
- Reservoir: It holds the hydraulic fluid that is used to transmit power within the system. The reservoir also acts as a heat exchanger, helping to dissipate heat generated during operation.
- Valves: Various valves control the flow, pressure, and direction of the hydraulic fluid. Examples include relief valves, directional control valves, and check valves.
- Filters: These components remove contaminants from the hydraulic fluid, preventing damage to the system components. Filters should be regularly inspected and cleaned or replaced as necessary.
- Heat Exchanger: It helps cool the hydraulic fluid in order to maintain optimal operating temperature and prevent the system from overheating. Regular maintenance of the heat exchanger is essential to ensure efficient cooling.
The operation of a hydraulic power unit involves the following steps:
- The hydraulic pump is activated, either manually or through an electric motor, and starts to create flow by drawing in fluid from the reservoir.
- The pump generates pressure in the fluid, which is then directed to the appropriate hydraulic components through valves and hoses.
- The hydraulic components, such as hydraulic cylinders or hydraulic motors, use the pressurized fluid to perform mechanical work. For example, a hydraulic cylinder extends or retracts, or a hydraulic motor turns a shaft.
Maintenance of a hydraulic power unit is crucial to ensure its optimal performance and longevity. Some key aspects of maintenance include:
- Regular inspection: Check for any leaks, damaged hoses, or loose connections. Inspect the fluid level and quality in the reservoir. Review the condition of filters and replace them as needed.
- Fluid maintenance: Regularly monitor the quality of the hydraulic fluid. Perform routine fluid analysis and change it at recommended intervals. Ensure the fluid is free from contaminants and meets the required specifications.
- Preventive maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for the power unit. This may include tasks such as lubrication, cleaning, and tightening of bolts and fittings.
- System cleanliness: Keep the surrounding area clean to prevent dirt and debris from entering the system. Regularly clean the reservoir and filters.
- Training and documentation: Provide proper training to operators and maintenance personnel. Keep detailed records of maintenance activities, including dates, tasks performed, and any issues identified.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure the reliable operation and longevity of your hydraulic power unit. However, it’s always recommended to refer to the manufacturer’s specific recommendations for your particular equipment.



One thought on “Hydraulic Power Unit”