Introduction with Meta TechX Engineers
The Role of Sulphur in Steel Making
Steel, a vital material in the modern world, is known for its strength, durability, and versatility. However, the quality of steel can be significantly influenced by various factors, including the presence of impurities. One such impurity, sulphur, plays a crucial role in the steel making process. In this article, we will explore the reaction between iron and sulphur during steel making, and how sulphur can affect the quality of steel in terms of both strength and weakness.
Iron and Sulphur Reaction
During the steel making process, sulphur present in the raw materials, such as iron ore, coal, and scrap metal, can react with iron to form iron sulphide. This reaction typically occurs during the melting or refining stages of steel production. The chemical equation for this reaction can be represented as:
Fe + S → FeS
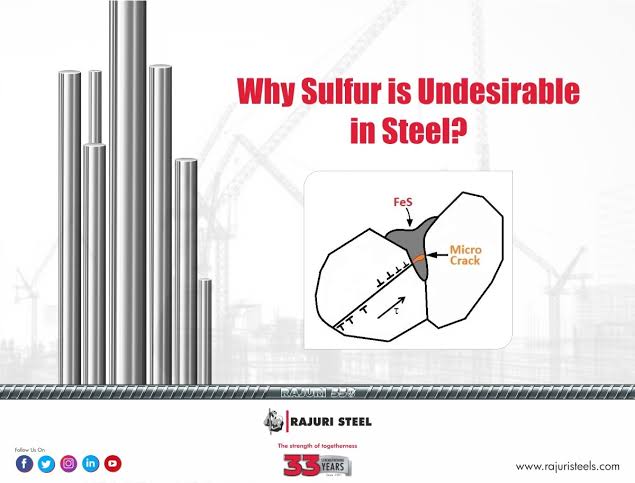
The formation of iron sulphide has a significant impact on the properties of steel, influencing its strength, ductility, and other mechanical characteristics.
Sulphur’s Effect on Steel Quality
Strength: Too Much of a Good Thing?
Sulphur can act as a strengthening agent in certain types of steel. In low-alloy and free machining steels, sulphur can improve the machinability and chip-breaking properties. However, an excess of sulphur can lead to detrimental effects on steel quality.
Brittleness: The Achilles’ Heel
High levels of sulphur in steel can significantly reduce its ductility, making it more prone to fracture and brittleness. This is particularly relevant in industries where toughness and resilience are critical, such as construction and automotive sectors. Therefore, controlling the sulphur content during steel making is crucial to avoid compromising the quality of the final product.
The Impact of Sulphur on Steel Strength and Weakness
To fully understand the impact of sulphur on steel quality, we must delve into the specific effects it has on steel strength and weakness.
Steel Strength
Sulphur, when present in controlled amounts, can contribute to the strength of certain types of steel. By enhancing the hardness and strength properties, sulphur allows for improved machinability and better chip formation during the manufacturing process.
However, it is essential to strike a balance, as excessive sulphur can result in the opposite effect. High sulphur content can promote the formation of iron sulphide inclusions, which act as stress concentration points in the steel matrix. These inclusions weaken the overall structure, reducing its tensile strength and potentially leading to premature failure.
Steel Weakness: Brittle Fracture
The presence of excess sulphur in steel can lead to a notorious weakness: brittleness. As sulphur content increases, it adversely affects the steel’s ability to deform plastically under stress. Instead, the steel becomes more susceptible to brittle fracture, meaning it is prone to sudden, catastrophic failure without undergoing noticeable deformation.
Brittle fractures can have severe consequences. In critical applications like structural components and machinery, the failure of steel due to excessive sulphur content can result in accidents, downtime, and expensive repairs. Therefore, keeping sulphur levels within acceptable ranges is essential to maintain steel’s desired properties.
Controlling Sulphur Content in Steel Making
To ensure the production of high-quality steel, sulphur levels must be carefully controlled during the steel making process. Several techniques can be employed to reduce sulphur content:
- Desulphurization: This involves using various agents, such as lime or magnesium, to react with sulphur and remove it from the molten steel. This process can be performed in the ladle or during refining.
- Scrap Selection: Careful selection of scrap or raw materials with low sulphur content can help minimize the overall sulphur concentration in the steel.
- Use of Flux: Fluxes like limestone or dolomite can be added to the furnace to facilitate the removal of sulphur during steel making.
- Temperature Control: Maintaining precise temperatures during the steel making process can help minimize the reaction between iron and sulphur, thereby reducing sulphur content.
By implementing these control measures, steel manufacturers can produce steel with optimal sulphur levels, ensuring its quality and performance.
Conclusion
In steel making, the presence of sulphur can significantly impact the quality of the final product. While controlled amounts of sulphur can enhance the strength and machinability of steel, excess sulphur can lead to brittleness and reduced ductility. Understanding the reaction between iron and sulphur, and employing effective desulphurization techniques, is crucial to ensure the production of high-quality steel. By maintaining optimal sulphur levels, manufacturers can create steel that meets the stringent demands of various industries and applications, ensuring durability, safety, and performance.