The Fascinating Process of Steel Making: Understanding Martensite Formation
Introduction with Meta TechX Engineers:
The Essence of Steel Making
Every day, we encounter numerous products made of steel, from household appliances to towering skyscrapers. But have you ever wondered how steel is produced and what gives it its remarkable strength? In the world of metallurgy, there is a crucial process known as steel making. In this article, we will delve deep into the realm of steel production, focusing specifically on the formation of a significant component called martensite.
The Formation of Martensite: Unraveling the Mystery
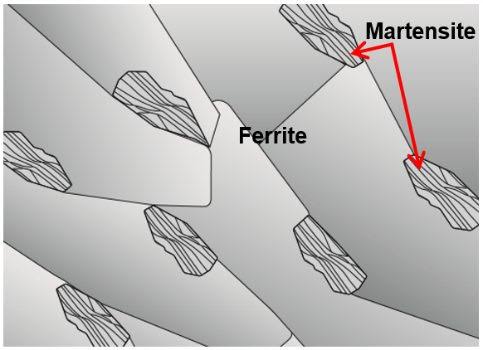
Martensite is a distinct microstructure that forms within steel during the cooling process. It possesses remarkable strength and hardness, making it a vital contributor to the overall properties of the steel. Typically, martensite is formed through rapid cooling, a process known as quenching, from austenite, another microstructure found in steel.
What is martensite in steel?
Martensite consists of a unique arrangement of atoms within the steel’s crystal lattice, giving it its distinctive properties. Unlike other microstructures such as ferrite and pearlite, which are relatively softer and ductile, martensite is exceptionally hard and brittle.
How does martensite formation take place?
The formation of martensite occurs when austenite is subjected to a rapid cooling process. It involves the transformation of the crystal structure from a face-centered cubic (FCC) arrangement to a body-centered tetragonal (BCT) structure. As the steel cools rapidly, the carbon atoms are trapped within the lattice, resulting in the formation of the strong and hard martensite microstructure.
The Key Factors Influencing Martensite Formation
Various factors play a crucial role in determining the formation and characteristics of martensite within steel. These factors include the carbon content, cooling rate, and alloying elements present in the steel.
Carbon content:
The carbon content within the steel significantly influences the propensity for martensite formation. Higher levels of carbon promote the formation of martensite, while lower carbon content can inhibit its formation. This is due to the carbon atoms’ ability to resist the crystal structure’s distortion during the transformation process, leading to the development of a harder and stronger microstructure.
Cooling rate:
The cooling rate during the quenching process is critical in determining the extent and quality of martensite formed within the steel. Rapid cooling rates, such as through the use of water or oil quenching methods, encourage the transformation of austenite into martensite. Slower cooling rates, on the other hand, promote the formation of softer microstructures like ferrite and pearlite.
Alloying elements:
The presence of alloying elements in the steel can significantly alter the characteristics of martensite. Elements like chromium, manganese, and nickel can enhance the steel’s hardenability, allowing for the formation of more martensite. These alloying elements also help in controlling the grain size of the martensitic microstructure, further improving the material’s overall properties.
Unlocking the Potential: Applications of Martensite
The exceptional strength and hardness of martensite make it a valuable component in various industries. Let’s explore some of the applications where martensite plays a vital role:
- Automotive Industry: Martensitic steel is commonly used in the manufacturing of engine components, such as crankshafts and gears, due to its high strength and wear resistance.
- Cutlery: Knives and blades made from martensitic stainless steel possess excellent cutting performance and corrosion resistance, making them a popular choice among chefs and professionals.
- Tool Manufacturing: Martensite is extensively utilized in the production of tools and dies, providing the necessary strength and hardness required for cutting, shaping, and precision work.
- Structural Applications: The construction industry relies on martensitic steel for structural components like beams and columns, as it offers superior strength and durability.
Conclusion: The Hidden Strength within Steel
Through the fascinating process of steel making, we uncover the secrets of martensite formation – a microstructure that instills steel with exceptional strength and hardness. By understanding the factors influencing martensite formation, we can harness its full potential and explore its diverse applications across various industries. From the automotive sector to tool manufacturing and beyond, martensite continues to shape our world, providing the backbone for countless structures and products we rely on every day.


Excellent post. I am experiencing some of these issues as
well..