Steel Industries: The Fueling Powerhouses
Introduction
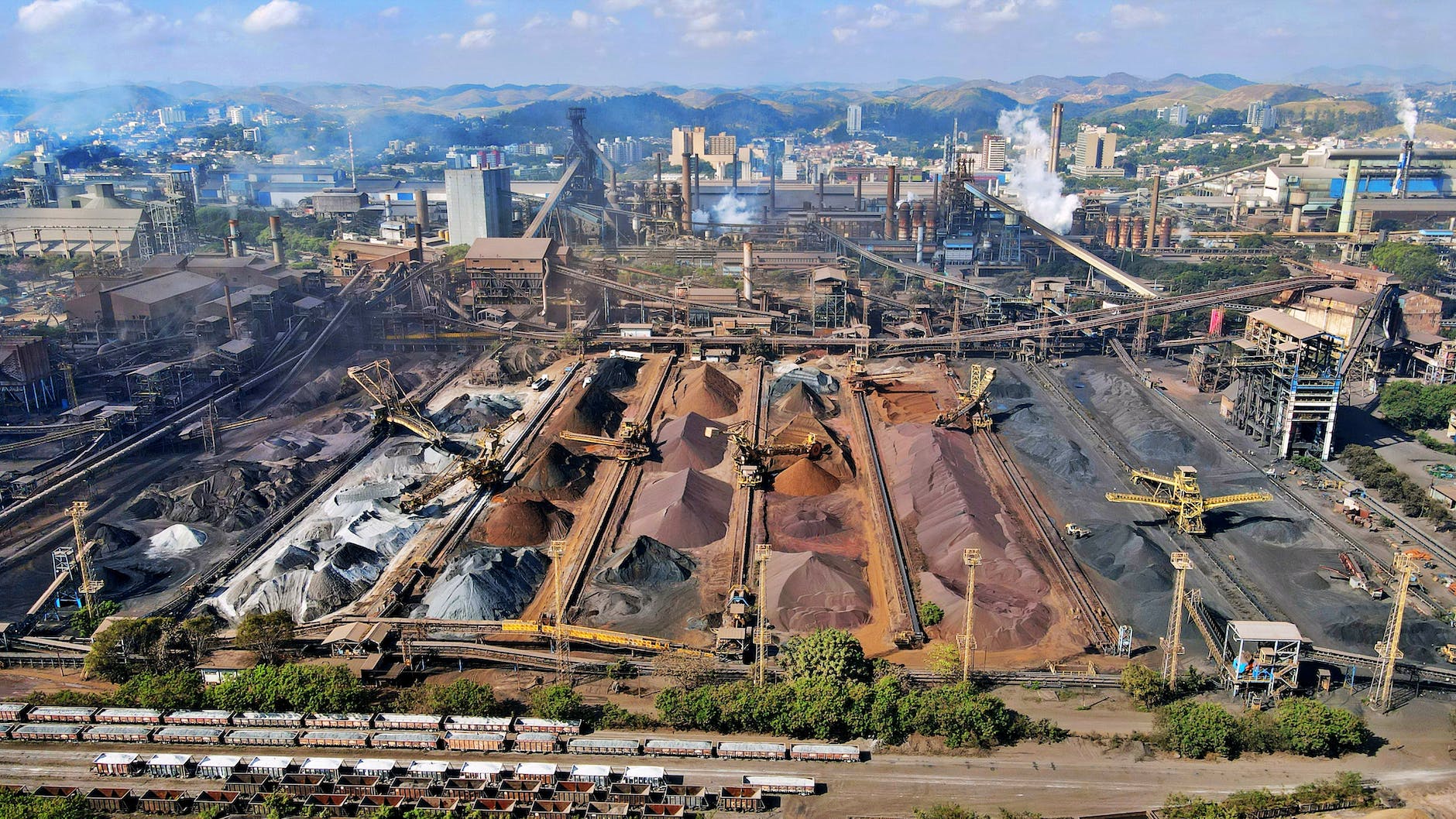
Steel is one of the most important and versatile materials known to humanity. It plays a vital role in various industries, from construction to manufacturing. The production of steel, however, is an energy-intensive process that requires a significant amount of fuel. Let’s explore with MetaTechX Engineers the different types of fuels used in steel industries, their efficiencies, and the best choice of environmentally friendly fuel for today and tomorrow.
Types of Fuels Used in Steel Industries
1. Coal
Coal has been the traditional fuel of choice in the steel industry for decades. It is widely available and relatively inexpensive. Additionally, coal can provide high temperatures required for steel production. However, the drawback of coal is its high carbon content, which contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. Despite these environmental concerns, coal still remains a significant fuel source in steel production due to its affordability and accessibility.
2. Natural Gas
Natural gas is becoming increasingly popular in the steel industry due to its lower carbon emissions compared to coal. It is a cleaner-burning fuel that produces less particulate matter and other pollutants. Natural gas also offers better controllability and efficiency during the steel manufacturing process. However, its availability and price can vary regionally, which may limit its widespread adoption in some areas.
3. Electricity
Electricity is another fuel option in steel production, particularly in electric arc furnaces (EAFs). EAFs use electricity to generate intense heat, melting scrap metal and transforming it into new steel products. This method eliminates the need for fossil fuels, resulting in reduced carbon emissions. However, the efficiency of electricity as a fuel source depends on the source of the electricity itself. If renewable sources like solar or wind power are used, it can further enhance the overall sustainability of steel production.
4. Hydrogen
Hydrogen is emerging as a promising fuel for the steel industry due to its potential for zero-carbon emissions. When used as a fuel in steel production, hydrogen produces only water vapor as a byproduct. It can be used as a direct replacement for coal or natural gas, making it a versatile and environmentally friendly option. However, widespread adoption of hydrogen in the steel industry requires significant research and investment to develop efficient and cost-effective production methods.
Fuel Efficiencies in Steel Industries
The efficiency of different fuels used in steel production can vary significantly. It is crucial to consider the energy conversion and overall greenhouse gas emissions when evaluating the efficiency of each fuel type. Here is a comparison of fuel efficiencies in the steel industry:
- Coal: Coal has a lower energy conversion efficiency compared to other fuels due to its high carbon content. However, advancements in technology, such as more efficient boilers and furnaces, have improved the overall efficiency of coal-fired steel plants.
- Natural Gas: Natural gas offers higher energy conversion efficiency compared to coal. Its clean-burning nature allows for better heat utilization and reduced energy losses during the steel manufacturing process.
- Electricity: Electric arc furnaces have relatively higher energy conversion efficiency due to the direct conversion of electrical energy into heat. However, the overall efficiency depends on the source and transmission losses of the electricity.
- Hydrogen: Hydrogen has the potential for high energy conversion efficiency when used in steel production. However, the current challenge lies in developing efficient hydrogen production methods and infrastructure.
The Best Choice of Environmentally Friendly Fuel
When it comes to choosing the best environmentally friendly fuel for today and tomorrow, it is essential to consider multiple factors, including carbon emissions, resource availability, and technological advancements. While natural gas offers lower carbon emissions compared to coal, it is still a fossil fuel and contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. Similarly, electricity can be a greener option if sourced from renewable energy, but its efficiency and availability may vary.
Hydrogen shows tremendous promise as a zero-carbon fuel for the steel industry. With further research and development, hydrogen can revolutionize the steel production process, eliminating carbon emissions entirely. However, it is crucial to address challenges such as large-scale hydrogen production and infrastructure development for its widespread adoption.
Conclusion
Steel industries play a vital role in our modern world, but their production process has significant environmental implications. As we strive for a more sustainable future, exploring alternative fuels and increasing energy efficiency in steel production becomes crucial. While coal and natural gas continue to be important fuel sources, the potential of electricity and hydrogen as cleaner alternatives cannot be overlooked. Embracing these environmentally friendly fuels will not only reduce carbon emissions but also ensure the longevity of the steel industry in a rapidly changing world.